by KD.Conway
TL;DR
-
Unified Liquidity Layer: By building both a DEX and a lending protocol on top of a unified liquidity layer, we enable liquidity in the AMM to be reused within the lending protocol. This maximizes capital efficiency.
-
Tradable Collateral and Debt: Leveraging the DEX and lending protocols, we make collateral and debt tradable assets. This adds flexibility, allowing users to more easily transfer or manage their collateral and debt positions.
-
Flexible Liquidation and Margin Trading: With a hook-based liquidation mechanism on the DEX, we support lending and margin trading for any token, enabling a wider range of assets to participate in DeFi markets.
Motivation
Currently, most assets in AMMs are underutilized, only a portion actually participates in trading, while the majority of funds remain idle. Take launch pads like pump.fun as an example: their liquidity pools hold around $4.5 billion worth of SOL, but these SOL tokens are only used for trading. If we could put the idle SOL in LPs to work—such as allowing others to borrow SOL—we could further boost both liquidity and capital efficiency. The same logic applies to other tokens, especially smaller tokens on various DEXs.
Furthermore, current lending protocols have limited flexibility. For example, if a user supplies USDC as collateral to borrow ETH for staking, they can’t easily adjust their collateral or debt positions until they fully repay the ETH. While some protocols offer flash loan mechanisms for more flexibility, these tend to be complex for regular users.
Unified Liquidity Layer
To solve these problems, we propose a unified liquidity layer—similar in design to Uniswap v4—where all funds are managed within a single contract. On top of this layer, we create two types of pools: a lending pool and a swap (DEX) pool.
-
DEX Pool: This pool supports token swaps and also provides liquidity for lending. By participating in the DEX pool, users earn both LP fees and lending interest, but they are exposed to impermanent loss.
-
Lending Pool: This pool manages funds that are not used for swaps, focusing solely on lending. Participants earn lending interest but are not exposed to impermanent loss or LP fees.
When users borrow tokens, the protocol prioritizes lending from the lending pool. Only when liquidity in the lending pool is insufficient does it tap into the DEX pool. Repayments follow the opposite order—repaying the DEX pool first, then the lending pool.
Lending x Swap: How It Works with Debt Token
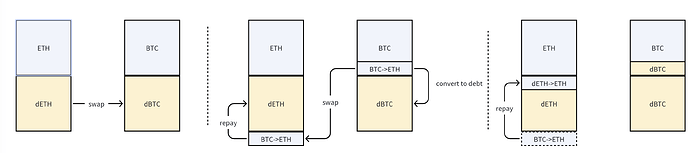
Consider a constant product AMM with two tokens, A and B, forming an A-B LP with a units of token A and b units of token B, such that a * b = k. We allow users to borrow either token from the pool. For example, if a user borrows a' units of token A, we introduce an “A debt token” (dA) into the LP to represent the loaned amount. The pool now has (a - a') of A tokens and a' of dA tokens, ensuring the total remains consistent: (number of A) + (number of dA) = a. This approach keeps the constant product formula intact: (number of A + number of dA) * (number of B + number of dB) = k.
This system allows users to borrow tokens directly from the AMM without disrupting regular trading activity. The only exception is when there’s not enough of a specific token available for a swap, in which case the user may receive the corresponding debt token instead and must wait for repayment to convert it back to the real token.
To prevent all liquidity from being borrowed out, we implement similar mechanisms as standard lending protocols: we cap the amount of tokens that can be borrowed from the LP, and borrowing costs (interest rates) increase as utilization rises. This incentivizes faster repayments and encourages more users to provide liquidity when it’s needed most.
Tradable Collateral and Debt
One of the standout features of our system is that both collateral and debt are fully tradable and transferable. This means your collateral and debt positions are highly liquid—you can swap or trade them at any time to maximize your benefits, or even let them passively generate income for you. Here’s how it works with a simple example:
Suppose a user supplies USDC as collateral and borrows ETH to participate in staking. In this scenario, the user’s collateral is USDC, and the debt is ETH.
Tradable Collateral allows users to flexibly change their collateral:
-
For example, if a user believes BTC will rise in value, they can swap their collateral from USDC to BTC. Now, their collateral is BTC and their debt is still ETH. If BTC appreciates, the user benefits from the price increase without having to repay their debt first.
-
Similarly, if USDT offers a higher lending rate than USDC, the user can convert their collateral from USDC to USDT, thereby earning more interest.
-
Users can also choose to convert their collateral into any other token pool. For instance, if they convert their USDC collateral into an LP of USDT and USDC, their collateral now provides liquidity for that pool. In this case, the user earns both lending interest and DEX trading fees from swaps involving that pool.
Tradable Debt enables users to flexibly adjust their liabilities:
-
For instance, if a user expects BTC to drop sharply and ETH to appreciate, they can swap their debt from ETH to BTC. Now, their debt is denominated in BTC. If BTC drops in value, the user effectively profits from the decline of their debt asset.
-
If borrowing ETH becomes too expensive, the user can switch their debt to a lower-interest asset, such as weETH, thereby reducing their borrowing costs.
-
Furthermore, users can split their debt into a basket of tokens (e.g., both ETH and weETH), allowing their debt to provide liquidity across multiple assets and potentially earn DEX trading fees, while spreading out their borrowing risk.
Implementation Details:
-
Tradable Collateral:
- If a user’s collateral is USDC and they want to convert it to BTC, this is simply executed as a single swap on the unified liquidity layer—swapping USDC for BTC.
-
Tradable Debt:
- If a user’s debt is ETH and they want to convert it to BTC, what happens under the hood is a transformation from dETH (ETH debt) to dBTC (BTC debt). This process involves swapping part of the BTC in the pool for ETH; the new ETH offsets the user’s ETH debt (decreasing dETH, increasing ETH in the pool), and BTC in the pool decreases while dBTC increases. The user doesn’t need to repay ETH immediately—they still hold ETH as an asset, but now owe BTC instead.
With this mechanism, both collateral and debt positions remain fully tradable, and users can freely convert them anytime without being locked in or forced to repay first. Collateral acts much like spot asset holdings, while debt resembles a short position. Combining collateral and debt into LPs enables the creation of “smart collateral” and “smart debt” like Fluid, unlocking new ways to generate value in DeFi.
Permissionless Lending & Margin Trading with Hook-Based Liquidation
Anyone can create a DEX pool, just like on Uniswap, and as soon as a pool is created, users can enable lending based on that pool. For major tokens like ETH or USDC, traditional lending protocols already provide solid support. However, for less popular tokens—say, an A token paired with ETH in a liquidity pool—we allow users to supply ETH as collateral and borrow A tokens (to short A), or supply A tokens and borrow ETH (to long A). Thanks to the unified liquidity layer, the ETH in these pools can also be lent out, further increasing capital efficiency.
For these lesser-known tokens, we don’t rely on external oracles for pricing. Instead, we use the price feeds directly from the DEX, implementing hooks that check for liquidation conditions before and after every swap. This means liquidation for small-cap tokens can happen automatically during regular DEX trading, ensuring fair and efficient risk management without external dependencies.
Conclusion
In summary, by introducing a unified liquidity layer and making both collateral and debt fully tradable, our system unlocks new levels of capital efficiency and flexibility for DeFi users. The integration of lending and Swap protocols allows users to maximize their assets, seamlessly manage their positions, and access new strategies that were previously impossible in traditional protocols. Permissionless lending, flexible margin trading, and on-chain liquidation further empower the community to build and participate in a more open, dynamic, and user-centric financial ecosystem. As DeFi continues to evolve, we believe these innovations will help drive the next wave of growth and adoption.