We have previously presented dType, a decentralized type system and extended the idea to Eth2. We also proposed a Cache Shard mechanism for highly used, common-good resources, like type definitions.
With dType, Cache Shard and Formality, any EE can benefit from formal type checking by having its types registered with dType and a type definition compatible with Formality.
Definitions
dType(EEx) is the implementation of dType corresponding to Execution Environment EEx.
EEt is an execution environment for Formality. It can interpret Formality code and has a dType(EEt) implementation which stores Formality type definitions with references to the shards that use those types.
Projected Use
Provides formal type management for all EEs. It is composed of dType(EEt) and Formality. dType interfaces EEt with any other EE as well as with the Cache Shard.
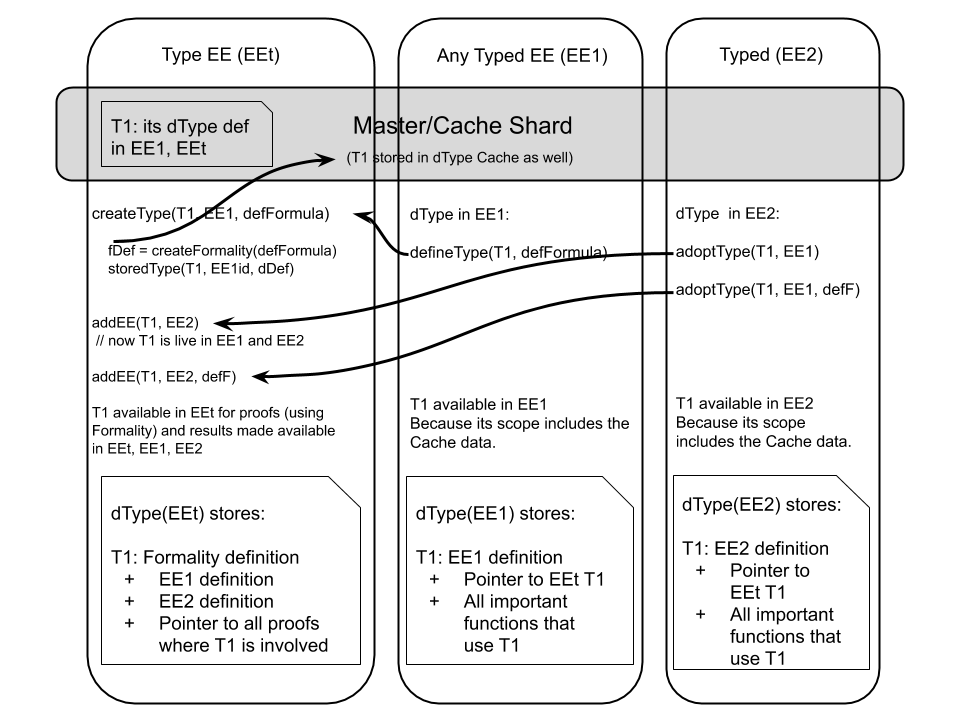
Suppose we have EE1, EE2, typed execution environments. If there is a need for a new type in EE1, a function defineType (deployed by dType with EE1 specifics) will be called with the formal definition for type T1 specific to EE1. This function will call the dType(EEt) createType with arguments:
Tid- proposed type identifierEEid- EE identifierdefFormula- formal definition ofTidforEEid.
Inside createType a Formality definition (specific to EEt) for the type T1 will be generated, stored with a mention that it is used by EE1 together with the definitions specific to EE1 and EEt.
EEt (Formality) will provide formal type checking for itself and all other typed EEs.
After T1 is stored in dType(EEt), a pointer to this item will be stored on the Cache Shard and EE1 will store that item also in dType(EE1). From this point forward, T1 type can be used in EE1 and EEt.
If another execution environment (EE2) smart contract needs to use a EE1 type, that has already been defined, adoptType can be called. If EE1 and EE2 are compatible and the EE1 T1 definition can be reused as-is on EE2, then adoptType(T1, EE1) can be called from EE2. Otherwise, a new defFormula for EE2 needs to be provided.
Notes:
- one might need a general type definition format, that bridges Formality definitions with other EE definitions.